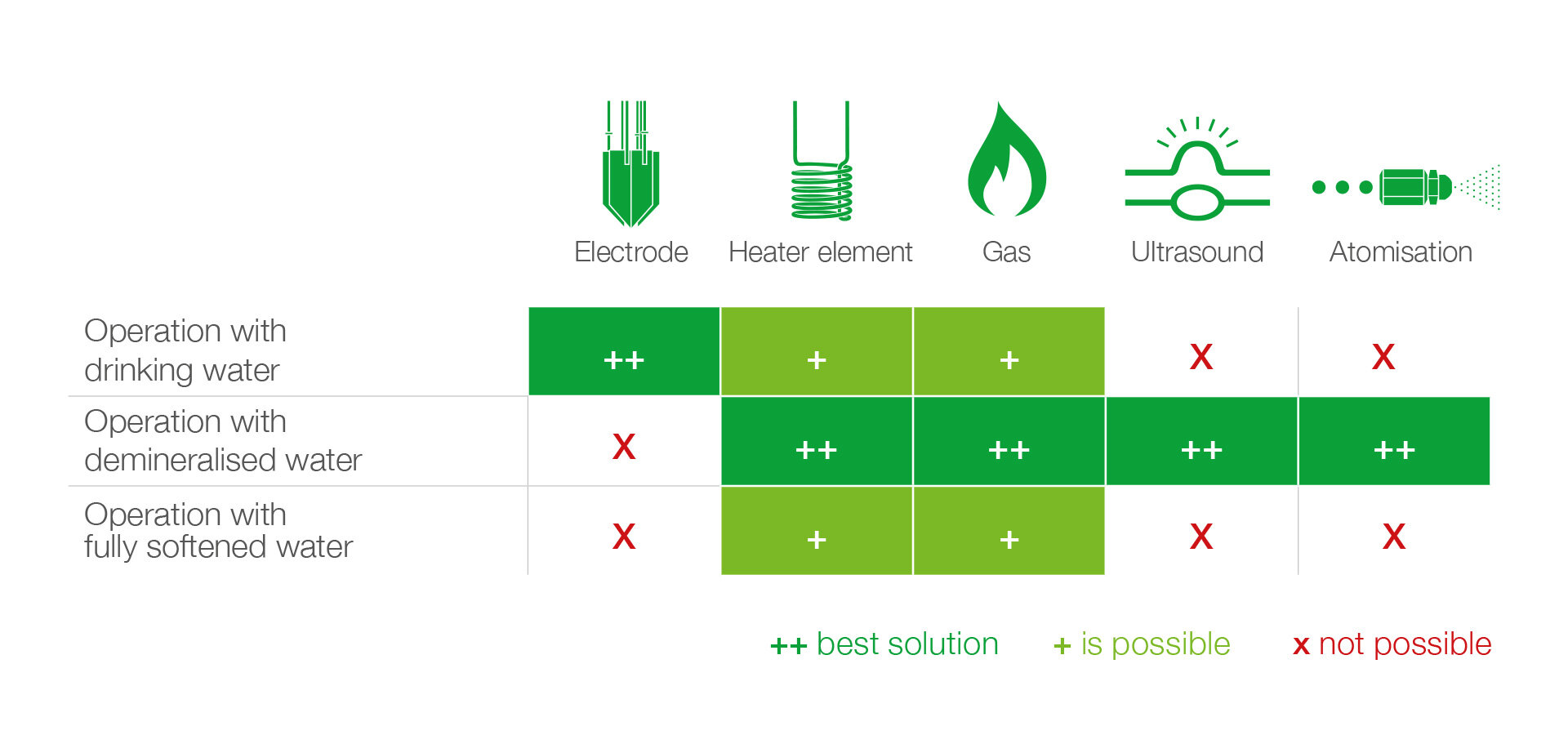
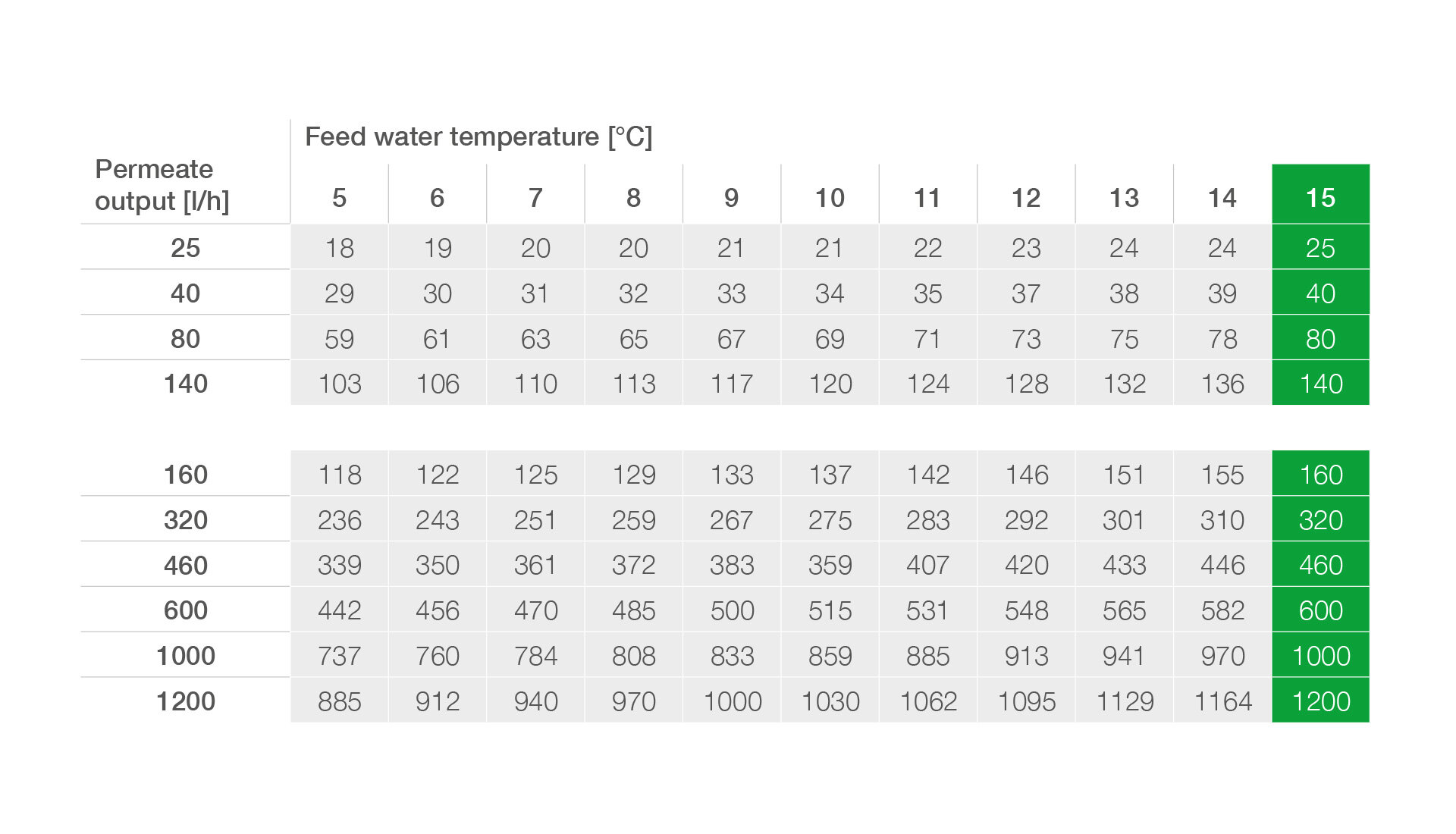
Planning information for osmosis systems
Expansion tanks are used as storage tanks and reduce the risk of pressure surges in the water pipes.
Rule of thumb for the expansion tank
The gross volume of the expansion tank (air content + water content) corresponds to approx. three times the net volume (buffer quantity or water content).
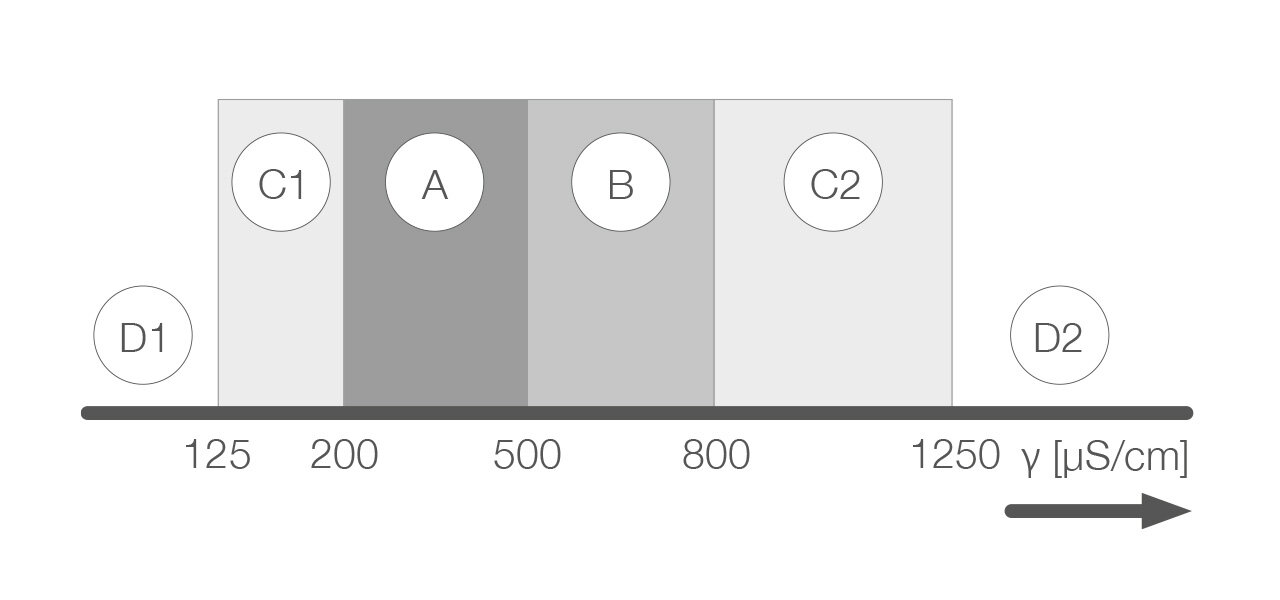
Rule of thumb conductance
approx. 35 times total hardness at 20 °C [µS/cm = 35 * ° dH]
- Osmosis systems with a lower capacity (up to 100 l/h) can usually be supplied with water up to 20 ° dH.
- For osmosis systems with higher capacities, softening or anti-scalant dosing is recommended.
- Do not forget the water analysis!