
Notes on electrode steam humidification
Observe water quality!
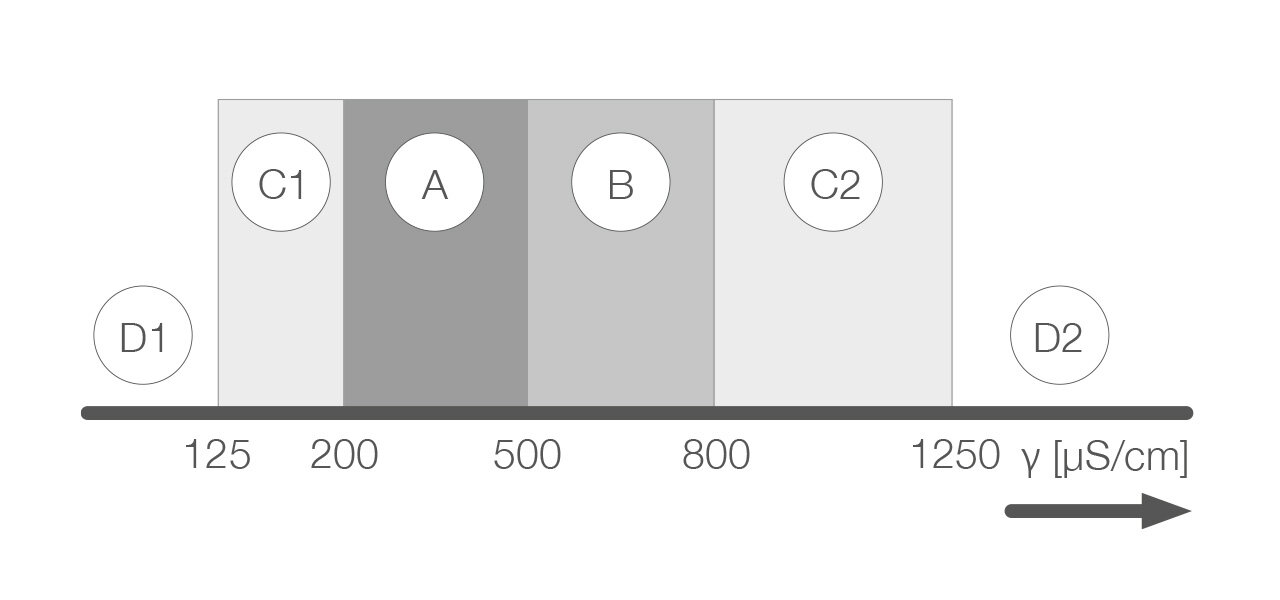
D1: Range below the operating limit
C1: Range of low conductivity
A: Range of normal conductivity
B: Range of increased conductivity
C2: Range of high conductivity
D2: Range above the operating limit
Avoid condensation as far as possible and minimise counterpressure!
- Few deflections
- Make wide bends
- Appropriately large pipe cross-sections
- Short hoses
- Insulated fixed piping is preferred
- Steam pipes should be laid with a gradient of 5 - 10%
Notes on heater type steam humidification
Observe water quality!
- Ideal demineralised water or at least softened
- Conductivity > 3 µS/cm
- Low total hardness
Avoid condensation as far as possible and minimise counterpressure!
- Few deflections
- Make wide bends
- Appropriately large pipe cross-sections
- Short hoses
- Insulated fixed piping is preferred
- Steam pipes should be laid with a gradient of 5 - 10%
Notes on gas steam humidification
Observe water quality!
- Ideal demineralised water or at least softened
- Conductivity > 3 µS/cm
- Low total hardness
Avoid condensation as far as possible and minimise counterpressure!
- Few deflections
- Make wide bends
- Appropriately large pipe cross-sections
- Short hoses
- Insulated fixed piping is preferred
- Steam pipes should be laid with a gradient of 5 - 10%
Notes on the spray nozzle system
Observe water quality!
- Demineralised 5 to 50 µS/cm
- Optimum temperature < 15 °C
- Dynamic flow pressure > 1 bar,
optimal > 2 bar
Air flow between 1.0 - 2.8 m/s input conditions!
- If possible, use enthalpy control
- The higher the inlet temperature and the lower the outlet humidity, the higher the efficiency

