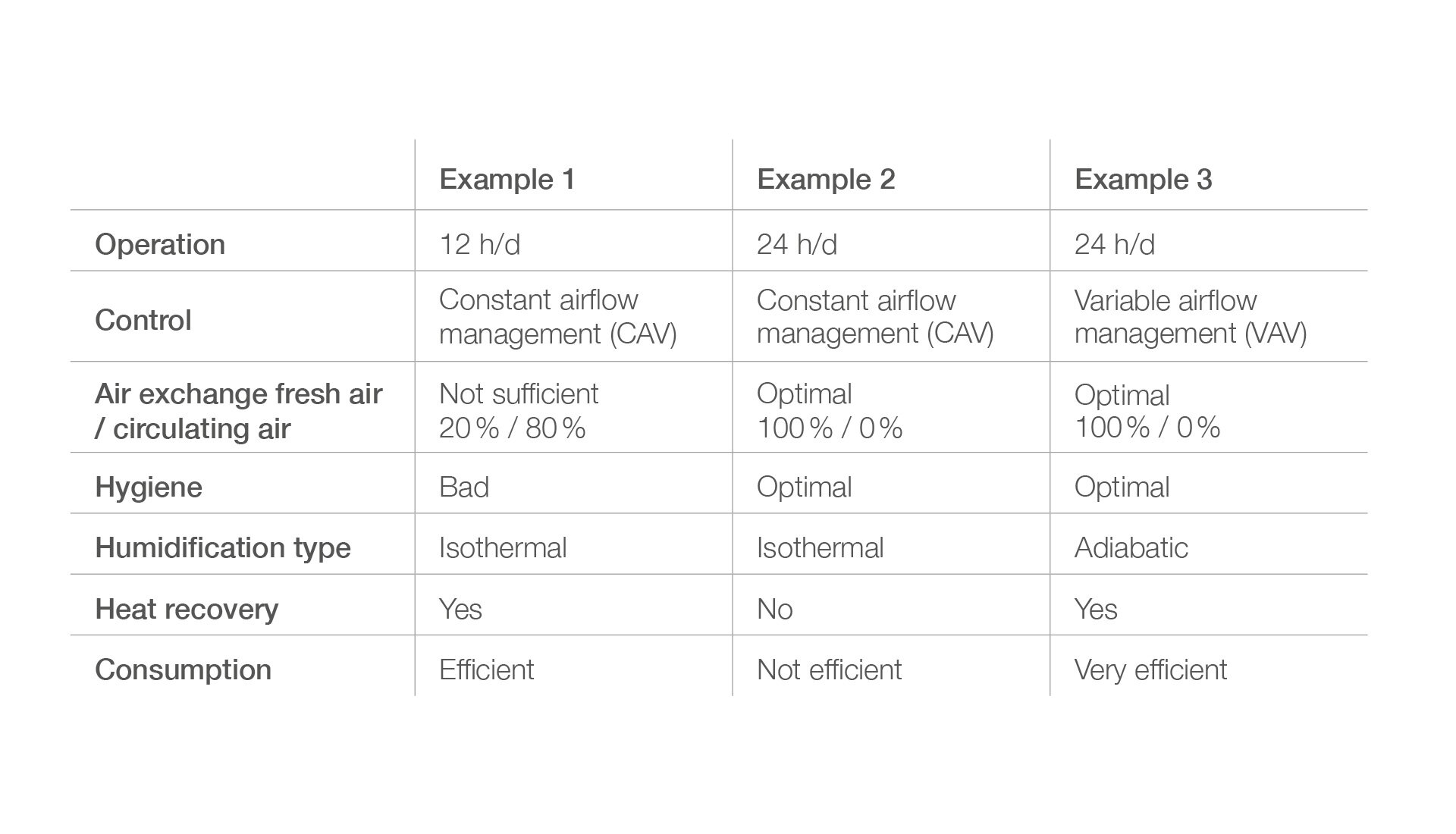
Operation 12 h/d | 20 % fresh air | with heat recovery - example 1
Operation 12 h/d | 20 % fresh air |
with heat recovery
Features
- Air flow Q = 31,600 m³/h
- Heat recovery ζ = 73 % sensitive, bypass on/off
- Isothermal humidification from electrical source
- Proportion of fresh air = 20 %
- Proportion of recirculated air = 80 %
- Constant airflow management (CAV)
- Operation 12 hours/day
Advantage: Efficient operation due to heat recovery
Disadvantage: No sufficient air exchange to reduce the virus load and lower the risk of infection
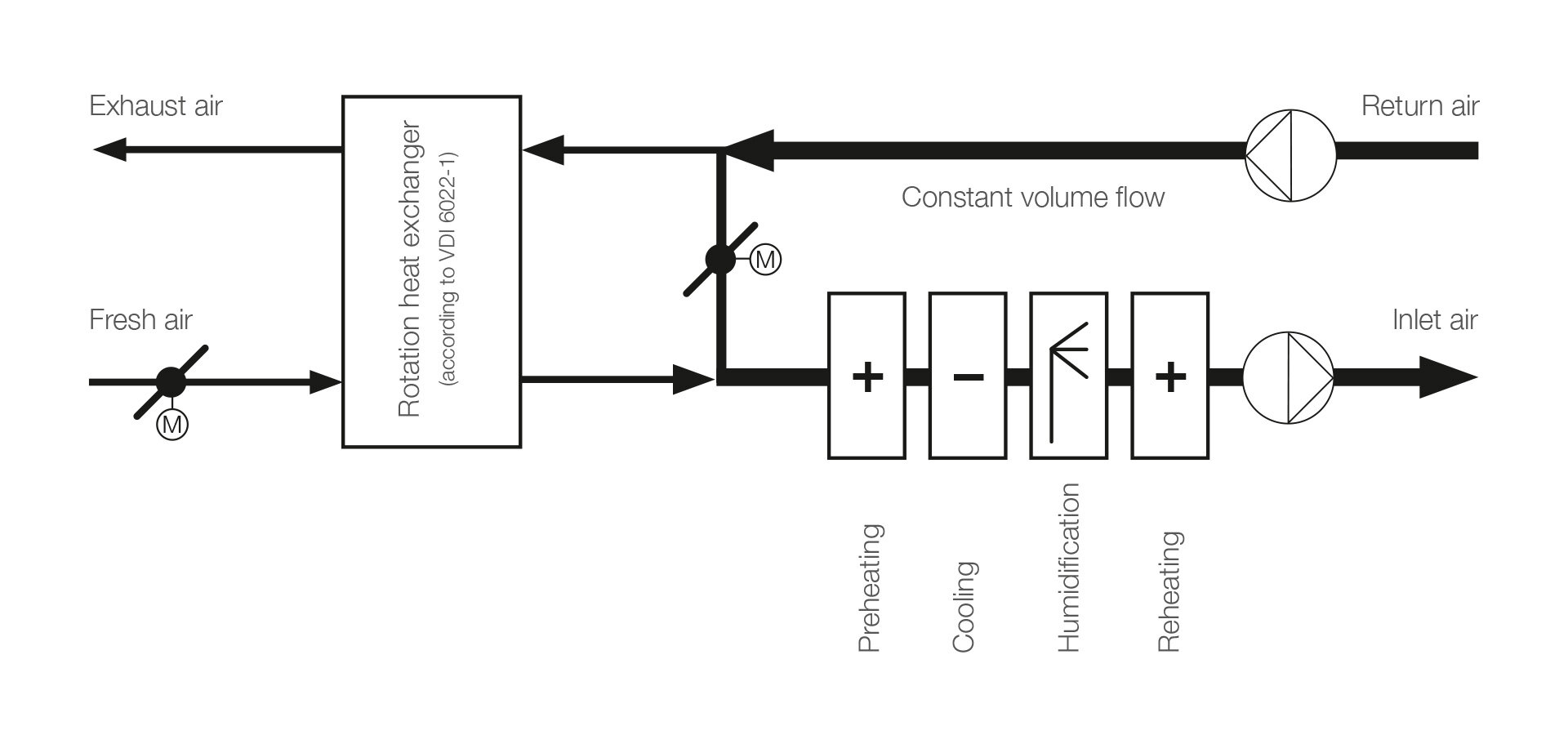
Operation 24 h/d | 100 % fresh air | without heat recovery - example 2
Operation 24 h/d | 100 % fresh air |
without heat recovery
Features
- Air flow Q = 31,600 m³/h
- Heat recovery deactivated (bypass)
- Isothermal humidification from electrical source
- Proportion of fresh air = 100 %
- Proportion of recirculated air = 0 %
- Constant airflow management (CAV)
- Operation 24 hours/day
Advantage: Optimal air exchange to reduce the virus load and lower the risk of infection
Disadvantage: No efficient operation, up to + 226 % higher total energy demand
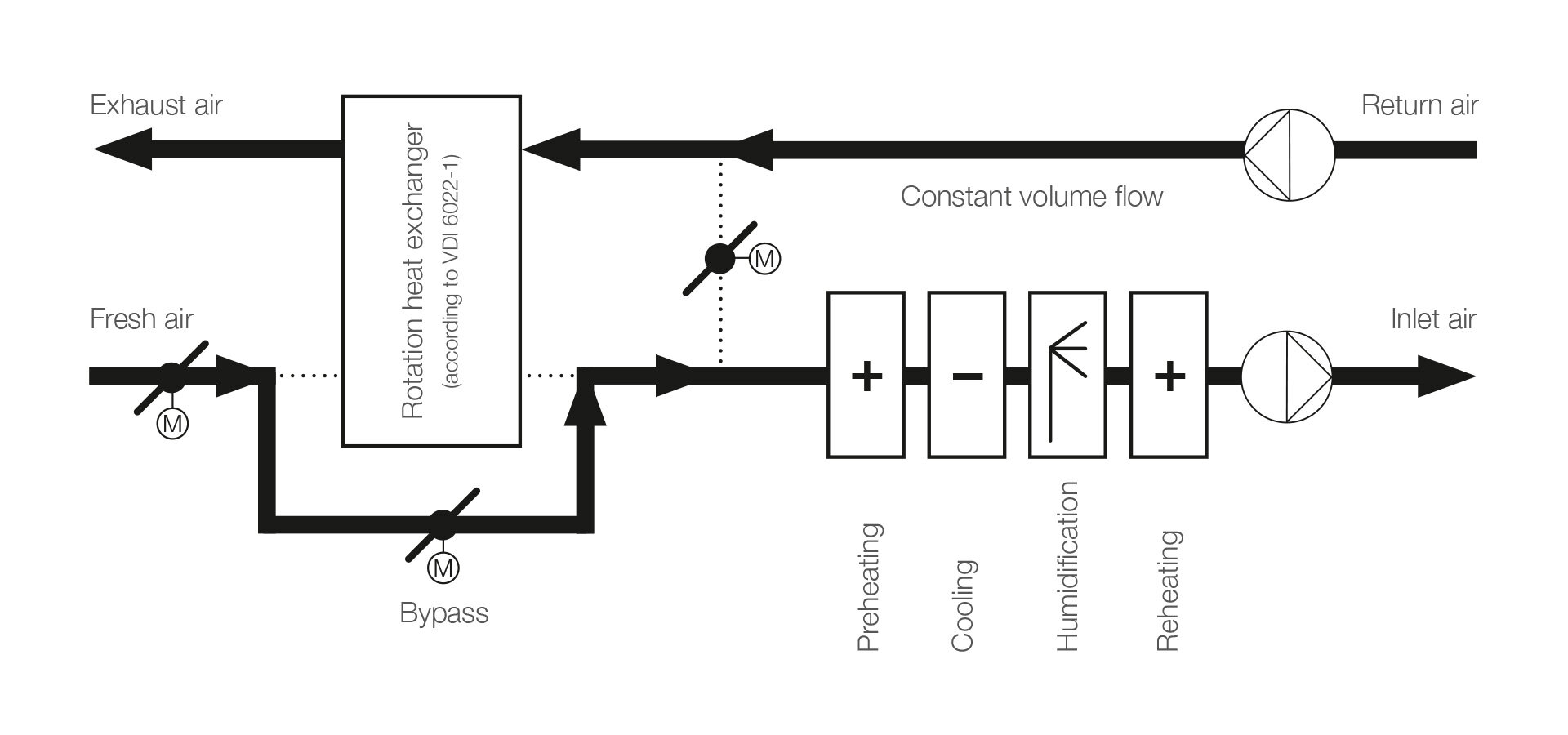
Operation 24 h/d | 100 % fresh air | with heat recovery - example 3
Operation 24 h/d | 100 % fresh air |
with heat recovery
Features
- Air flow Q = 31,600 m³/h
- Heat recovery ζ = 73 % sensitive, bypass on/off
- Adiabatic humidification
- Proportion of fresh air = 100 %
- Indirect evaporative cooling with humidity recovery
- Proportion of recirculated air = 0 %
- Variable airflow management (VAV)
- Operation 24 hours/day
Advantage: Efficient operation through heat recovery with optimum air exchange to reduce the virus load and lower the risk of infection

